Meningitis is an infection in the nervous system. It can be caused by bacteria and virus or complication from neurosurgery, trauma, and infection in sinus or ears.
Meningococcal meningitis occurs in epidemic form and transmitted by droplet infection from nasopharyngeal sections. Viral meningitis is associated with viruses such as mumps, paramyxovirus, herpes virus, and enterovirus.
The diagnoses of meningitis is made by testing cerebrospinal fluid that shows increased pressure, cloudy, high of protein, and low glucose.
Signs and Symptoms:
- There are no classic signs and symptoms. It depends on the type, child age, and duration of illness.
- Vomiting and diarrhea
- Fever, chills
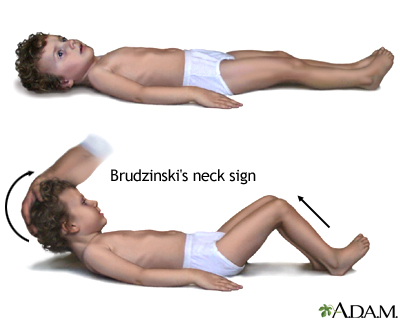
- Nuchal rigidity
- Poor feeding or anorexia
- Alter level of consciousness
- Bulging anterior fontanel in infant
- Muscle or joint pain
- Kernig's sign and Brudzinski's sign
Nursing Intervention:
- Isolation for at least 24 hours after antibiotic initiated
- Administer antibiotics as prescribed
- Assess neurological and cardiovascular system
- Monitor intake and output